Whether you're studying engineering, exploring manufacturing processes, or just curious about how precise metal parts are made - this is your guide to understanding chemical etching. We’ve broken down the basics, added examples, and included links to more advanced topics when you're ready to dive deeper.

Curious about how metal etching works or where it fits in the real world? This page is your entry point. Follow the links below to explore the process, materials, and real-life uses - at your own pace, no experience needed.
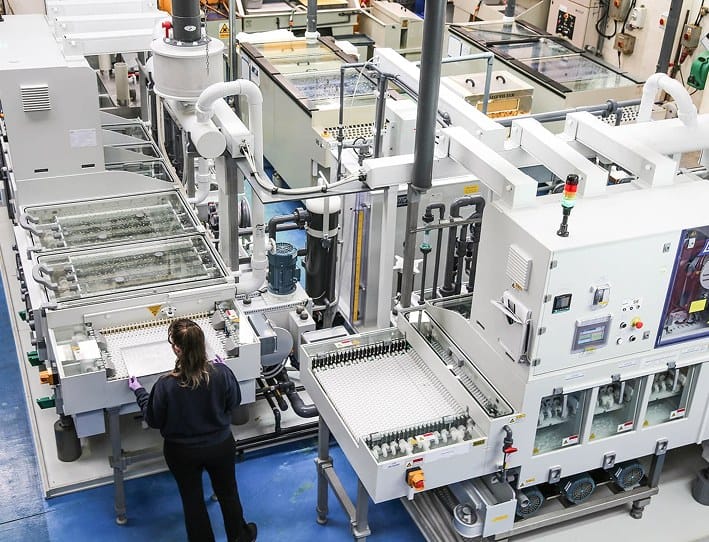

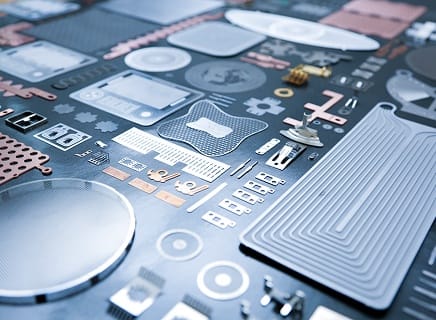
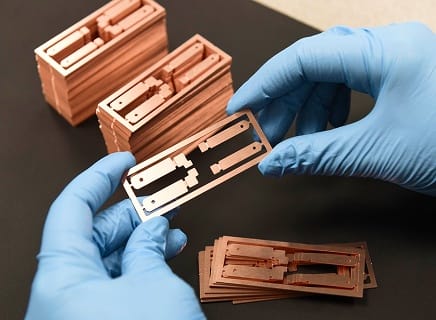



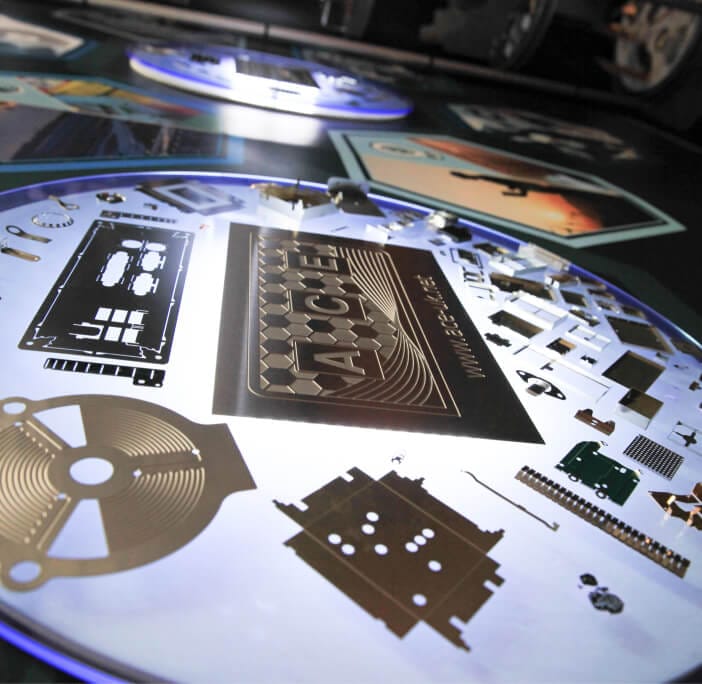
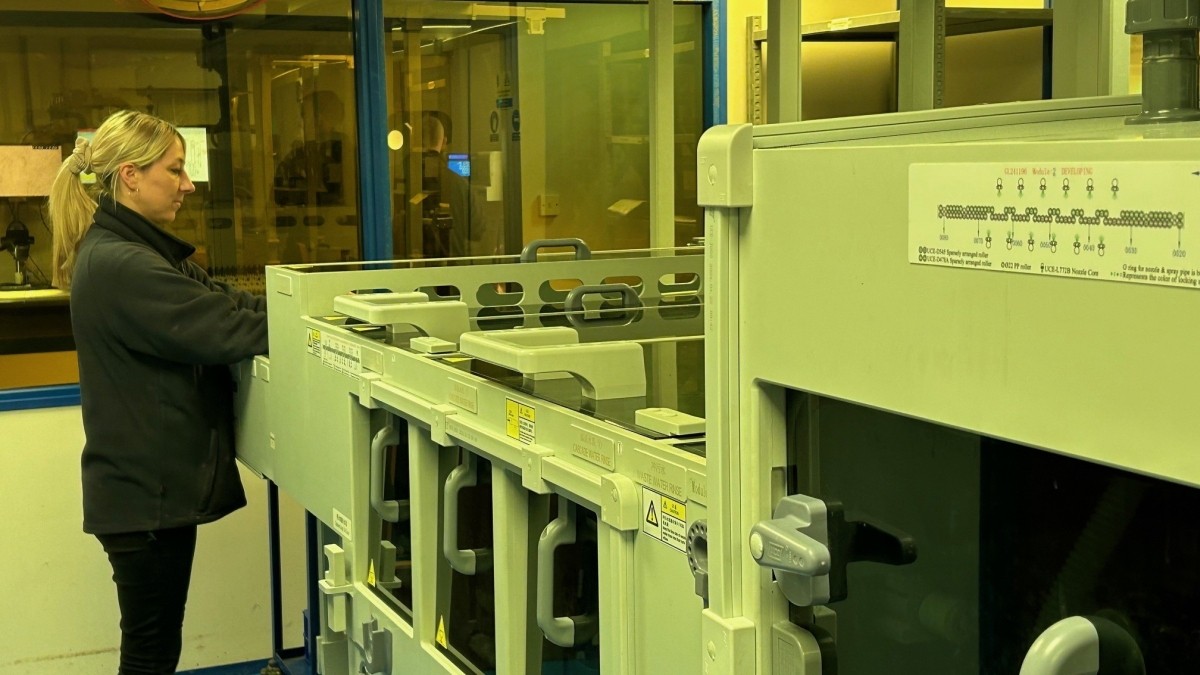
A precise, clean way to cut metal.
Using chemistry instead of tools.
Chemical etching (sometimes called photo etching) is a way of cutting very fine shapes into metal using a chemical reaction, not drills, blades, or lasers.
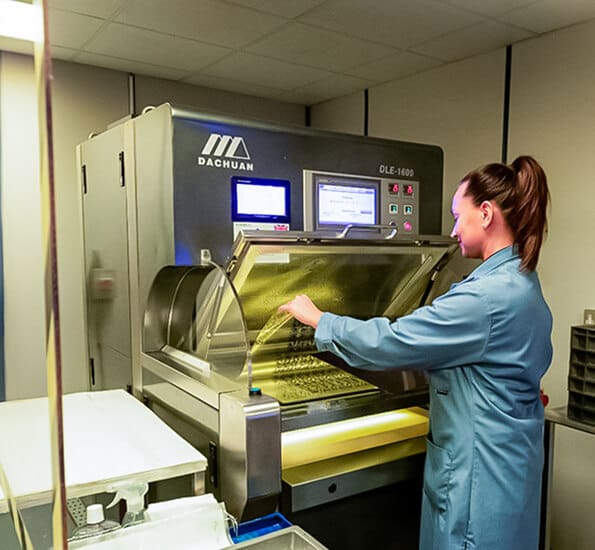
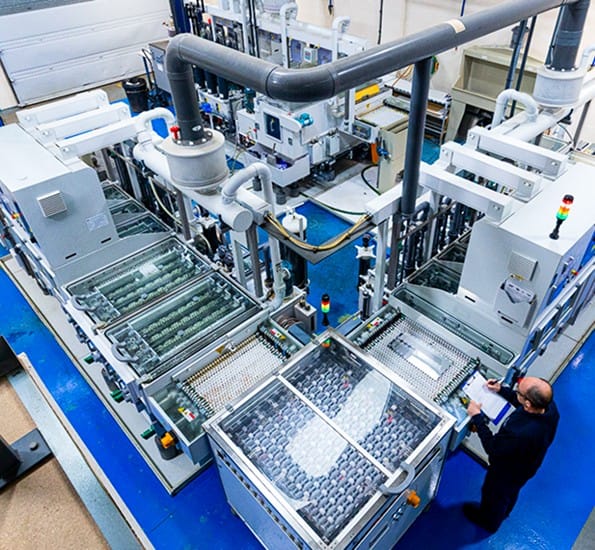
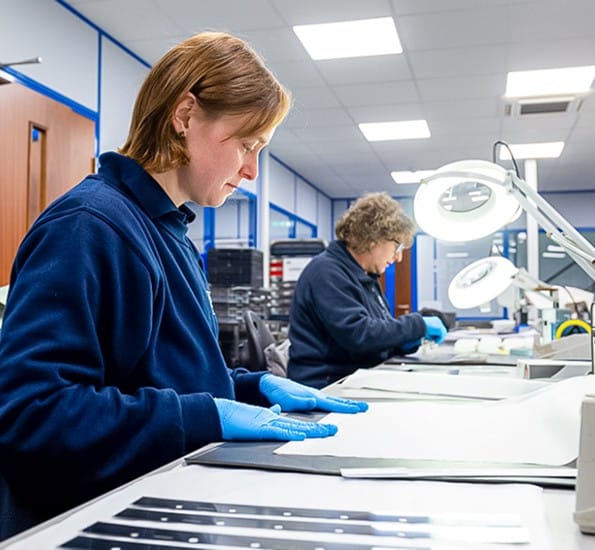




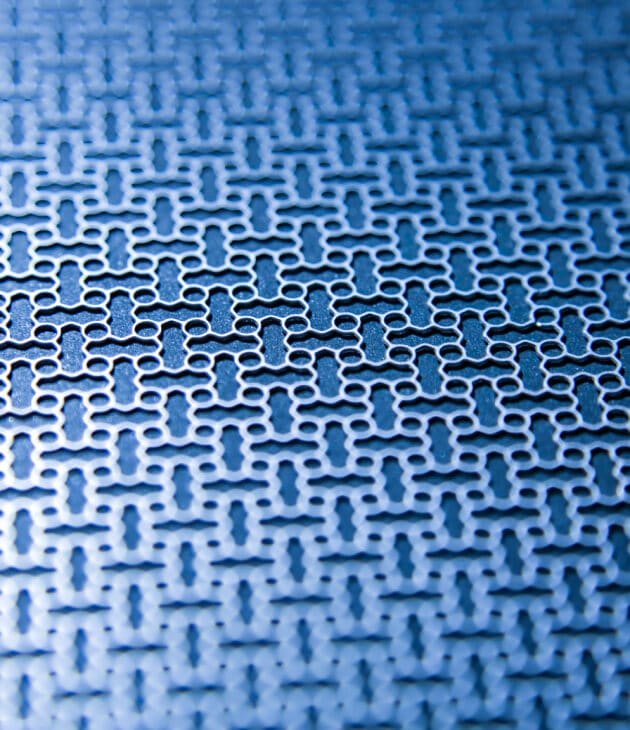
Good Question!
Unlike CNC or laser cutting, chemical etching doesn’t use force. or heat - so there’s no warping, no burrs, and no need for expensive tooling. It’s cleaner, faster for thin parts, and great for intricate designs that other methods struggle with.
Go Deeper - Compare Metal Etching With Other Methods
From aircraft to headphones - etched parts are everywhere.
Chemical etching is used to make all kinds of precision metal parts, many of which you’ve probably seen (or used!) without even realising it.
Because the process is so precise, clean, and flexible, it’s ideal for parts that are thin, detailed, or delicate - especially when made in large numbers. It’s widely used in industries like aerospace, electronics, automotive, and healthcare, but also turns up in day-to-day tech, wearables, and even design objects.
Examples of etched components:
Etched parts are flat, but that doesn’t mean they’re simple. In fact, many are packed with detail you can only see up close.
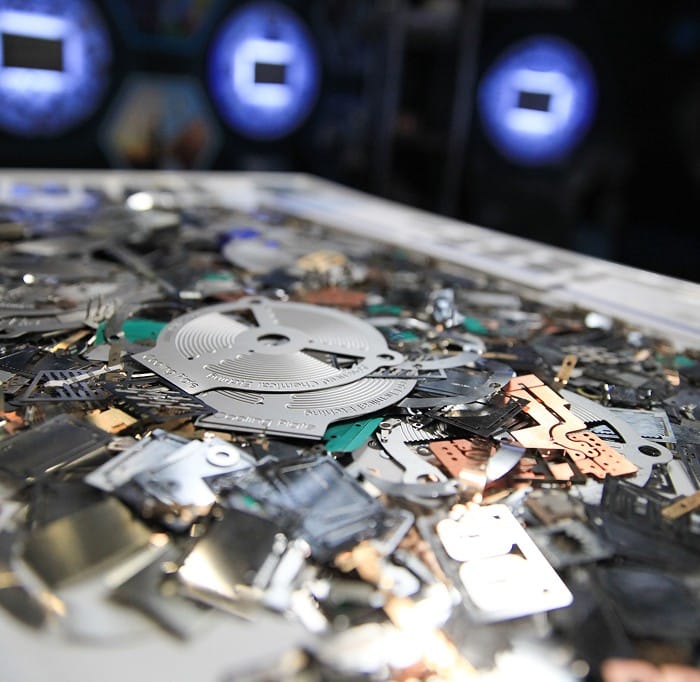
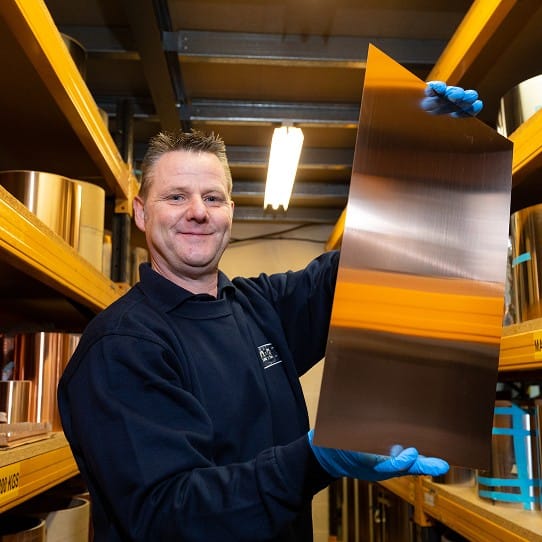
Copper, stainless steel, titanium, and more. It’s not just one-size-fits-all.
One of the strengths of chemical etching is that it works with a wide variety of metals, each suited to different jobs. That means engineers and designers can choose the right material based on what the part needs to do - whether that’s conduct electricity, resist heat, or just stay lightweight.
You don’t need to choose alone. The ACE team can recommend the best metal for your idea or application.

What it’s like to work with ACE - from first sketch to finished part.
Turning an idea into a finished metal part might sound high-tech, but the basic steps are actually easy to follow - especially with the help of ACE’s engineers.
Here’s a simplified version of the process:



From beginner basics to advanced insights - explore at your own pace.
If you’re the kind of person who likes to keep digging, we’ve got you covered. Whether you’re a student researching manufacturing processes, a hobbyist experimenting with electronics, or just someone who wants to know how things are made - we’ve got deeper content ready for you.
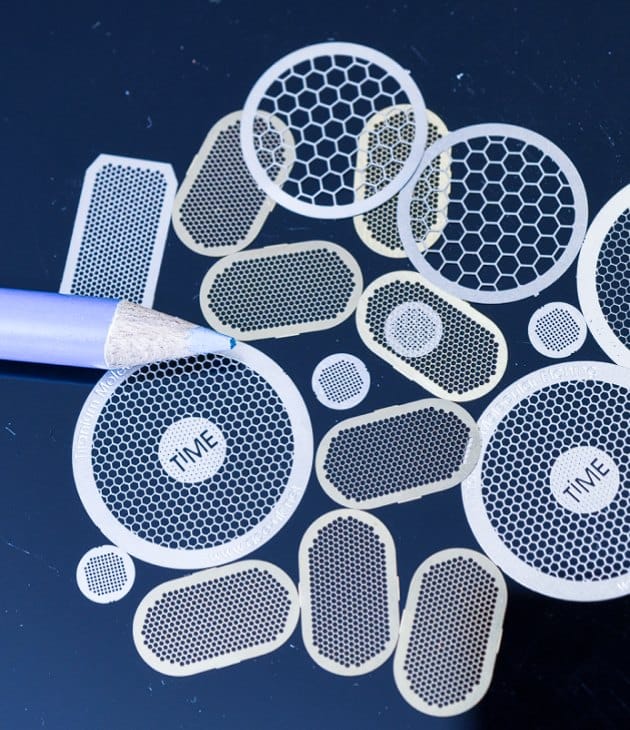
check our knowledge base
Explore technical guides, common questions, sample information, and detailed case studies.
Product Components
See examples of real parts we etch—like shielding, springs, mesh, and more.
Industries We Serve
Learn how ACE supports aerospace, automotive, electronics, medical, and more.
Quality & Accreditations
See how we meet ISO and AS9100 standards, and why it matters.


